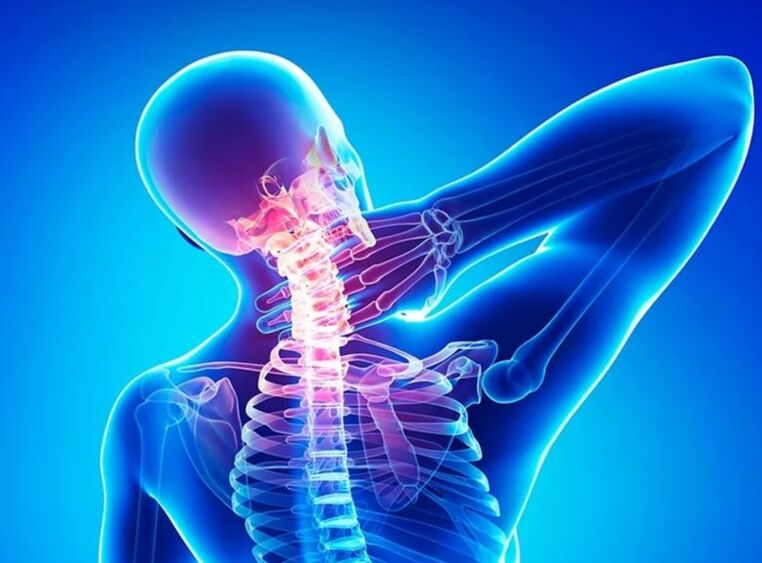
DESCRIPTION OF DISEASE
Osteochondrosis is a pathological condition of spinal bone tissue.The disease is characterized by dystrophic changes and a decrease in the function contained in the intervertebral discs.The pathology provokes the exacerbation of the fixed ability of the spinal column due to a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, as well as a decrease in vertebral muscle tone and ligaments.
Some forms of osteochondrosis are distinguished depending on the localization of the dystrophic changes: cervix, chest, lumbar, sacral.One of the most common is cervical osteochondrosis (up to 25% of the total).The disease accompanies unpleasant sensations that significantly reduce the quality of human life.
It is worth noting that cervical osteochondrosis can occur at any age.At the moment, the disease is often diagnosed with school students and students, which is accompanied by a sedentary lifestyle and long -term stay on computer and textbooks (subject to the wrong body position).
In the absence of treatment, osteochondrosis progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced, complications often occur: intervertebral hernia, nerve pliers, blood circulation, hypoxia, etc.
Symptoms
With cervical osteochondrosis, insufficient nutrition of the intervertebral discs of the cervical region occurs, from which they become fragile, and the distance between them is greatly reduced.At the same time, bone tissue becomes prone to growth and formation of bone growth (osteophytes).In later stages, growths move and begin to squeeze the tissues, vessels and nearby nerves that occur in the cervical region.
Cervical osteochondrosis- Chronic, gradually developing disease.Therefore, the symptoms of pathology at different stages are different.
- Symptoms of first -degree osteochondrosis
In the initial stage of the disease, there is a small decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc of the cervical back.Pathology has mild symptoms.There is discomfort in the neck, which can spread to the shoulders.In some cases, neck pain can occur, manifested in physical activity. - Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree of
At this stage, the height of the disk continues to decrease, there is incorrectly increasing tissue of cartilage, elongation develops.Acques can form in the fibrous ring.The pain begins to intensify, becomes longer, can radiate to the hands and along the spine.There is a sensation of rigidity with the curves of the neck, a cramp and the appearance of headaches is possible. - Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree
In the 3rd stage of the disease, a fibrous ring and the formation of intervertebral hernias are broken.The spinal column is deformed, displacements or vertebrae subluxation may occur.The patient feels acute pain, prolonged neck, numbness, partial loss of sensitivity of skin areas in the nape, neck, shoulder or hands. - Symptoms of osteochondrosis of 4th degree
At an advanced stage of the disease, irreversible changes occur - multiple osteophytes develop, intervertebral disc structures are gradually replaced by scar fabrics.The resulting hernia suppressing blood vessels and nerves, a person has organs hypoxia, pathology of the circulatory system.The pain lasts for a long time, the neck and upper shoulder strap become immobilized, the quality of life deteriorates significantly.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, the patient may have symptoms such as headaches, noise or bell in the ear, nausea, various visual impairment (shooting, darkening, pain).
Reason
Cervical osteochondrosis occurs due to improperly distributed load on the cervical spine.At the same time, the neck muscles cannot withstand mechanical pressure, spasm, which leads to circulatory disorders.From this, degenerative changes come to the upper back.
Factors that contribute to the development of cervical back osteochondrosis:
- hereditary predisposition;
- neck damage;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- Long stay in a position - on the computer, driving, etc.;
- The presence of autoimmune diseases is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus,
- scleroderma;
- violation of metabolism;
- the presence of endocrine diseases - gout, diabetes;
- Excessive body weight.
Troubleshooting
If there is a doubt about the presence of cervical osteochondrosis, it is necessary to contact a medical institution in a timely manner.Comprehensive diagnosis will help identify the disease, assess its degree and understand the causes of pathology development.A preliminary diagnosis is made on the basis of inspection and palpation - with osteochondrosis, the tension of the cervical muscles is observed, in some cases deformation of the spine is visible.
After objective diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient to additional studies.
The following diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Magnetic resonance tomography;
- Radiography (side and right);
- Multi -layer calculated tomography.
To determine the cause of the development of the pathology, an ultrasound examination of nearby organs, ECG of the heart, duplex scan of blood vessels, blood tests and urine can also be prescribed.
Therapeutic treatment
With the timely detection of cervical osteochondrosis, the disease is given well the therapeutic treatment.Unfortunately, osteochondrosis cannot be fully cured, however, therapy will help prevent further development of the disease, relieve unpleasant symptoms and normalize the mobility of the upper pole.
The following methods are used for this:
- Drug treatment.Medications relieve pain and inflammation, restore blood circulation and eliminate cramps in the neck muscles.For this, the following drug groups can be used: glucocorticosteroids, analgesics, slow -acting drugs, muscle relaxants, etc.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment.In addition to taking medication to relax the cervical muscles, eliminate cramps and normalize blood circulation will help physiotherapeutic procedures: massage, acupuncture, laser effect, magnetotherapy, UHF therapy, phonoforesis, etc.
- Therapeutic gymnastics.Special physical exercises will help the patient strengthen the muscle frame, approximate behavior and improve blood supply to the top of the spinal column.
Surgical treatment
In the case of advanced stages of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine or with insufficient effectiveness of conservative methods, surgery is required.
The following methods of surgery can be used depending on a specific clinical case:
- Small invasive removal of vertebral hernia.
- Laminectomy is an operation to remove vertebral processes.
- Removing a hernia and stabilizing the operated segment using a system consisting of four titanium screws and two peaks of rods.
- Endoscopic removal of a hernia.



















